




















MOLCAS manual: Next: 8.31 mknemo Up: 8. Programs Previous: 8.29 mclr
|
| File | Contents |
| JOBPDFT | This file is written in binary format and has the same structue of the JOBIPH file. |
| RUNFILE | The RUNFILE is updated with information from the MC-PDFT calculation. |
| MCDENS | This ASCII file is generated for MC-PDFT calculations. It contains spin densities, total density and on-top pair density values on grid (coordinates in a.u.). |
8.30.3 Input
This section describes the input to the
MCPDFT program in the MOLCAS program system. The input starts
with the program name
&MCPDFT
The KSDFT is the only required keyword.
| Keyword | Meaning |
| KSDFT | The functional choice follows. Currently available functionals are: tPBE, tBLYP, tLSDA, trevPBE, ftPBE, ftBLYP, ftLSDA, and ftrevPBE. |
8.30.3.1 Input example
The following example shows the input to the
RASSCF and MCPDFT programs for a calculation on the water molecule.
The tPBE functional is used. The calculation is
performed in C2v symmetry (symmetries: a1, b2, b1, a2, where the two
last species are antisymmetric with respect to the molecular plane). Inactive
orbitals are 1a1 (oxygen 1s) 2a1 (oxygen 2s) and
1b1 (the 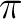 lone-pair orbital). Two bonding and two anti-bonding
OH orbitals are active, a1 and b2 symmetries. The calculation is
performed for the 1A1 ground state. Note that no information about basis set,
geometry, etc has to be given. Such information is supplied by the
SEWARD integral program via the one-electron integral file ONEINT.
lone-pair orbital). Two bonding and two anti-bonding
OH orbitals are active, a1 and b2 symmetries. The calculation is
performed for the 1A1 ground state. Note that no information about basis set,
geometry, etc has to be given. Such information is supplied by the
SEWARD integral program via the one-electron integral file ONEINT.
&RASSCF
Title= Water molecule. Active orbitals OH and OH* in both symmetries
Spin = 1
Symmetry = 1
Inactive = 2 0 1 0
Ras2 = 2 2 0 0
&MCPDFT
KSDFT=TPBE
The first RASSCF run is a standard CASSCF calculation that leads to variationally optimized orbitals and CI coefficients. The MC-PDFT run will use the orbitals and density matrices optimized during the preceeding RASSCF run.
Next: 8.31 mknemo Up: 8. Programs Previous: 8.29 mclr

