




















MOLCAS manual: Next: 8.16 ffpt Up: 8. Programs Previous: 8.14 expbas
|
| Keyword | Meaning |
| TITLe | One-line title. |
| FRAGment | Takes one, two or three argument(s). The first value (integer) defines the fragment number, the second value (real) determines coefficient, and the third value (integer) is the fragment number that is equivalent to this fragment when translational symmetry is used. A default for the second value is 1.0 where the first and third values have no default. Other keyword(s) specific to this fragment must follow this keyword. |
| OPERator | A real value following this keyword represents a coefficient, Cifragment, of fragment i (current fragment), where i is a value specified by FRAGMENT keyword. This keyword is equivalent with the second value of keyword, FRAGMENT. |
| EQUIvalence | An integer, j, following this keyword declares that current fragment is translationally equivalent with fragment j, and information provided for fragment j are tranfered to current fragment. This keyword is equivalent with the third value of keyword, FRAGMENT. |
| TRANslate | Three real numbers following this keyword specifies the translational vector by which the current fragment is translated to give new coordinate. A unit of either bohr or angstrom can follow. The default unit is angstrom. This keyword takes effect only when the equivalent fragment is specified. |
| RUNFile | Following this keyword specifies the name of RunFile file for the corresponding fragment. |
| ONEInt | Following this keyword specifies the name of OneInt file for the corresponding fragment. |
| NFRAgment | An integer following this keyword specifies the number of fragments. If this keyword is not given, the largest fragment number given by FRAGMENT keyword is set to be the number of fragment. |
| NIRRep | An integer following this keyword specifies the number of irreducible representation of point group symmetry. |
| OCCUpation | A list of integer(s) following this keyword specifies the number of occupied orbitals in each symmetry representation in the unfragmented system. |
| DISTance | A real number following this keyword specifies the distance of two atoms that are equivalent to each other, followed by a unit that is eather angstrom or bohr. Default is angstrom. |
| NEAR | A real number following this keyword specifies the distance of two atoms within which atoms are considered to be too close each other. An unit that is eather angstrom or bohr can follow. Default is angstrom. |
| An integer following this keyword specifies the format of orbital print out. | |
| ORBEne | A real number follwing this keyword stands for the threshold for orbital print out. The orbitals with orbital energy below this value are print out. |
| ORBOcc | A real number follwing this keyword stands for the threshold for orbital print out. The orbitals with occupation number above this value are print out. |
8.15.2.2 Input examples
Below shows an example of input file for the three fragment system of which
energy, Ewhole, is written as
by fragment energies, E1fragment, E2fragment, and E3fragment.
&FALCON
Fragment=1, 1.0
Fragment=2, 1.0
Fragment=3, -1.0
which can be simplified as,
&FALCON
Fragment=3, -1.0
The next example is a two fragment system in which fragment 1 and fragment 2 are equivalent except for their positons. When their difference in position is described by a vector, (1.0, 1.0, -1.0), a translational symmetry can be used and the input becomes as follows,
&FALCON
Fragment=2, 1.0, 1
Translate=1.0, 1.0, -1.0
If the total energy of the whole system is given by the sum of total energies
of three fragment,
input is simplly as follows,
&FALCON
nFragment=3
Next: 8.16 ffpt Up: 8. Programs Previous: 8.14 expbas


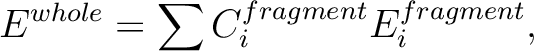
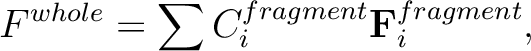
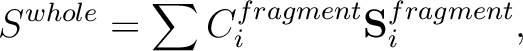
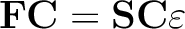
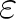 .
.