MOLCAS manual:

Next: 7.3 General input structure. EMIL
Up: 7. The MOLCAS environment
Previous: 7.1 Overview
Subsections
This section will describe the usage of MOLCAS in an
UNIX environment.
Production jobs using MOLCAS in an UNIX environment can be
performed as batch jobs.
This requires the creation of a shell script that
contains a few simple commands. Further you need to create input for
each program module that you intend to use. This section describes the
necessary steps you have to take in order to make a successful job using
MOLCAS.
Input examples for a typical MOLCAS run can be found in doc/samples/problem_based_tutorials/ directory.
Also you can use some input examples
in Test/input subdirectory.
There is a command supplied with the MOLCAS package, named
molcas, that the user issue to perform a given task.
A sequence of such commands will perform the calculation requested by
the user.
| Command | Purpose
|
| molcas | This command tells which MOLCAS installation will be used, and gives
some help about usage of MOLCAS command
|
| molcas input-file | This command executes a command in the MOLCAS system.
|
| molcas help prgm | This command gives the list of available keywords for program prgm.
|
| molcas help prgm keyword | This command gives description of a keyword.
|
| molcas help environment | This command gives a list of MOLCAS specific environment variables.
|
| molcas help basis element | This command gives a list of basis sets available for an element.
|
The following is an example of running MOLCAS by using a single input file:
molcas $Project.input
An alternative way of running MOLCAS as a sequence of separate calls:
molcas $Project.seward.input # Execute seward
molcas $Project.scf.input # Execute scf
By default, the output will go directly to the screen. If can be redirected
by using flag -f, e.g. molcas -f water.inp will store the output
in water.log and water.err files.
The default behavior of MOLCAS execution can be altered by setting environment variables.
When running a project, MOLCAS uses the variable
Project giving a project name, and a scratch directory defined by
the variable WorkDir.
This serves the purpose of maintaining structure of the files and
facilitating automatic file mapping.
There are several ways to set up these variables.
By default, the name of the Project constructed from the name of the input file,
by removing the last suffix, e.g. for example for an input name Water.SCF.input
the Project name will be Water.SCF.
Alternatively,
user can set environment variable Project, or MOLCAS_PROJECT.
Scratch directory can be set by environment variable MOLCAS_WORKDIR.
If it is set to value "PWD", current directory will be used. Otherwise,
it can be set to a directory name. In this case scratch area will be located
in a subdirectory $MOLCAS_WORKDIR/$Project. It is also possible to
overwrite the value of scratch area, by setting environment variable
WorkDir.
- Project=
 ; export Project ; export Project
- WorkDir=
 ; export WorkDir ; export WorkDir
MOLCAS modules communicates between each other via files, located in the WorkDir.
The description of internal filenames and file mapping can be found at Appendix.
When you have decided which program modules you need to use to perform your
calculation, you need to construct input for each of these. There is no
particular structure enforced on the input files, but it is recommended that
you follow:
- $Project.``prgm-name''.input
which is the name of the input files assumed in the sample shell script.
When you prepare a job for batch processing, you have to create a shell script.
It is recommended that you use the sample shell script supplied with
MOLCAS as a starting point when building your own shell script.
The following steps are taken in the shell script:
- Define and export the MOLCAS variables
- Project (or use
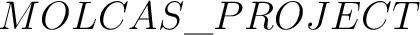 ) )
- WorkDir (or
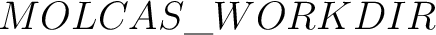 ) )
- Issue a sequence of MOLCAS commands.
- Remove the scratch directory and all files in it.
The following is an example of a shell script.
Project=HF; export Project # Define the project id
WorkDir=/temp/$LOGNAME/$Project.$RANDOM; export WorkDir # Define scratch directory
molcas $Project.input # Run molcas with input file, which
# contains inputs for several modules
rm -r $WorkDir # Clean up
The file $ThisDir/$Project.input contains the ordered sequence
of MOLCAS inputs and the EMIL interpreter will call the appropriate
programs. See section ![[*]](crossref.png) for an explanation of the
additional tools available in the EMIL interpreter. for an explanation of the
additional tools available in the EMIL interpreter.
The following is an example of a shell script to be submitted for batch
execution.
Project=HF; export Project # Define the project id
WorkDir=/temp/$LOGNAME/$Project.$RANDOM; export WorkDir # Define scratch directory
molcas $Project.seward.input # Execute seward
molcas $Project.scf.input # Execute scf
rm -r $WorkDir # Clean up
An alternative way to control teh usage of the WorkDir is to use flags in molcas command:
| Variable | Purpose
|
| -new | clean WorkDir before the usage
|
| -clean | clean WorkDir after the usage
|
Note, that if you configured your working environment by using setuprc script,
the only command you have to place into the shell script is:
molcas $Project.input
7.2.5 System variables
MOLCAS contains a set of system variables that the user can
set to modify the default behaviour of MOLCAS. Two of them
(Project and WorkDir) must be set in order to make MOLCAS work at all.
There are defaults for these but you are advised not to use the defaults.
There are several ways of using MOLCAS environment variables:
- These variables can be exported in your shell script
export MOLCAS_MEM=512
molcas input
- These variables can be included into MOLCAS input:
* begin of the input file
>>> export MOLCAS_MEM=512
. . .
- variables can be included directly into molcas command in the form:
molcas MOLCAS_MEM=512 input
The simplest way to set up default environment for MOLCAS is
to use script setuprc, which can be run as command
molcas setuprc. This interactive script creates
a resource file molcasrc, located either in 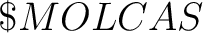 or or
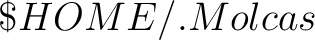 directory. The priority of these settings is: user defined settings
(e.g. in molcas command), user resource file, MOLCAS resource file.
directory. The priority of these settings is: user defined settings
(e.g. in molcas command), user resource file, MOLCAS resource file.
Two flags in MOLCAS command are related to resource files:
| Variable | Purpose
|
| -env | Display current MOLCAS environment
e.g. molcas -env input will print information about environment
variables, used during execution of the input file.
|
| -ign | Ignore resource files
e.g. molcas -ign input will process input file without settings,
which are stored in
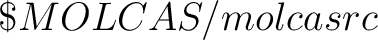 and in and in
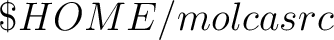 files. files.
|
The most important environment variables, used in MOLCAS:
| Variable | Purpose
|
| Project | This variable can be set in order to overwrite the default name of the
project you are running. The default (and recommended) value of the project name is the
name of the input file (without the file extension).
|
| WorkDir | This variable can be used to specify directly the directory where all files
that MOLCAS creates are placed. See MOLCAS_WORKDIR for more options.
|
| CurrDir | This variable corresponds to the location of the input, and it is used as
a default location for all output files, generated by MOLCASmodules.
|
| MOLCAS | This variable indicates the location of MOLCAS. The default version of Molcas
to be used is specified at file .Molcas/molcas, located at user HOME directory.
|
| MOLCAS_NPROCS | This variable should be used to run MOLCAScode in parallel. It defines the
number of computational units (cores or nodes) which will be used.
|
| MOLCAS_MEM | This environment variable controls the size (soft limit) of the
work array utilized in the programs that offer dynamic memory.
It is specified in Megabytes, i.e.
MOLCAS_MEM=256; export MOLCAS_MEM
will assign 256Mb for the working arrays.
It is also possible to use Gb (Tb) to specify memory in Gb or Tb.
- MOLCAS_MEM is undefined — The default amount of memory (2048MB),
will be allocated for the work arrays.
- MOLCAS_MEM is defined but nonzero — This amount of memory
will be allocated.
See also MOLCAS_MAXMEM.
|
The complete list of MOLCAS-related environment variables:
| Variable | Purpose
|
| MOLCAS_COLOR | By default molcas uses markup characters in the output. To overwrite, set the key to NO.
|
| MOLCAS_NPROCS | See above
|
| MOLCAS_DEBUGGER | This variable can be set to the name of debugger (or another code) which will be used on top of
molcas executables. The option is useful for tracing an error in the code
|
| MOLCAS_DISK | The value of this variable is used to split large files into a set of
smaller datasets, as many as are needed (max. 20 subsets). It is specified
in Megabytes, for instance, MOLCAS_DISK=1000; export MOLCAS_DISK,
and the following rules apply:
- MOLCAS_DISK is undefined — The program modules will ignore this
option and the file size limit will be defined by your hardware
(2 GBytes for 32-bit machines).
- MOLCAS_DISK=0 (zero) — The programs will assume a file size limit
of 2 GBytes (200GBytes on 64-bit machines).
- MOLCAS_DISK is defined but nonzero — The files will be limited to
this value (approximately) in size.
|
| MOLCAS_ECHO_INPUT | An environment variable to control echoing of the input.
To suppress print level, set MOLCAS_ECHO_INPUT to 'NO'.
|
| MOLCAS_FIM | Activates the Files In Memory I/O layer. See section ![[*]](crossref.png) for more details.
Note that this setting is available only in MOLCAS compiled without Global
Arrays. for more details.
Note that this setting is available only in MOLCAS compiled without Global
Arrays.
|
| MOLCAS_GRID | Seward, SCF, RASSCF can compute (screen quality) grid automatically.
If set to AUTO, only the last program in the input will compute grid.
Yes - force the code always compute grids (it might take time)
No - disable the automatic generation of grids.
|
| MOLCAS_KEEP_WORKDIR | If set to NO MOLCAS will remove scratch area after a calculation.
This setting can be overwritten by running molcas with flag -clean.
|
| MOLCAS_LICENSE | An environment which specifies the directory with MOLCAS license file license.dat.
The default value of this variable is directory .Molcas/ in user home directory.
|
| MOLCAS_LINK | An environment variable to control information about linking of files.
By default (MOLCAS_LINK is not set) only essential
information about linking will be printed. To increase/decrease the
print level, set MOLCAS_LINK to 'Yes'/'No'.
|
| MOLCAS_MAXITER | An environment variable to control maximum number of iterations in DO WHILE loop.
|
| MOLCAS_MAXMEM | An environment variable to set up a hard limit for allocated memory (in Mb).
If is not specified, then it takes value of MOLCAS_MEM. Otherwise, the (MOLCAS_MAXMEM-MOLCAS_MEM)
amount of RAM will be primarily used for keeping files in memory (FiM), or allocating Distributed Global Arrays.
Note that this setting is available only in MOLCAS compiled without Global Arrays.
|
| MOLCAS_MEM | See above.
|
| MOLCAS_MOLDEN | If MOLCAS_MOLDEN set to 'ON' a Molden style input file will be generated regardless of the number of orbitals.
|
| MOLCAS_NEW_WORKDIR | If set to YES MOLCAS will never reuse files in scratch area.
This setting can be overwritten by running molcas with flag -old:
molcas -old input
|
| MOLCAS_OUTPUT | This variable can alter the default directory for extra output files,
such as orbitals files, molden files, etc.
If set, MOLCAS will save output files to the specified directory.
The directory name can be set in the form of absolute PATH, or
relative PATH (related to the submit directory).
A special value 'WORKDIR' will keep all output files in WorkDir.
A special value 'NAME' will create a subdirectory with a name of Project.
If the variable is not set, all output files will be copied or moved
to the current directory. Default value can be forced by MOLCAS_OUTPUT=PWD.
|
| MOLCAS_PRINT | MOLCAS_PRINT variable controls the level of output. The value could be numerical or mnemonic:
SILENT (0), TERSE (1), NORMAL (2), VERBOSE (3), DEBUG (4) and INSANE (5).
|
| MOLCAS_PROJECT | If set to value NAME, MOLCAS will use the prefix of the input file
as a project name. Otherwise, it set a project name for the calculation.
If set to the value NAMEPID, the Project name still will be constructed
from the name of input file, however, the name of scratch area will
be random.
|
| MOLCAS_PROPERTIES | If MOLCAS_PROPERTIES is set to 'LONG' properties with the individual MO contributions will be listed.
|
| MOLCAS_REDUCE_PRT | If set to NO, print level in DO WHILE loop is not reduced.
|
| MOLCAS_REDUCE_NG_PRT | If set to NO, print level in numerical_gradient loop is not reduced.
|
| MOLCAS_SAVE | This variable can alter the default filenames for output files.
If not set (default), all files will overwrite old files.
If set to 'INCR' all output files will get an incremental
filenames.
If set to 'ORIG' - an existent file will be copied with
an extension '.orig'
|
| MOLCAS_TIME | If set, switch on timing information for each module
|
| MOLCAS_TIMELIM | Set up a timelimit for each module (in minutes). By default, the maximum
execution time is set to unlimited. Note that this setting is available only
in MOLCAS compiled without Global Arrays.
|
| MOLCAS_TRAP | If MOLCAS_TRAP set to 'OFF' MOLCAS modules will continue to be executed,
even if a non-zero return code was produced.
|
| MOLCAS_WORKDIR | A parent directory for all scratch areas. It can be set to an
absolute PATH (recommended), to a relative PATH, or to a special value PWD
(to use current directory for scratch files)
|
User can customize his installation by adding MOLCAS environment variable into molcasrc file.
Another way of customizing MOLCAS is to use prologue and epilogue scripts. If user created a file
prologue in $HOME/.Molcas directory it will be executed (as ./prologue) before MOLCAS calculation
starts. epilogue in $HOME/.Molcas directory will be executed at the end of calculation.
Files module.prologue and module.epilogue contains commands executing before and after
each executable molcas module. These files may use internal Molcas variables, such as
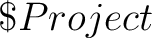 , , 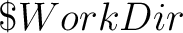 , , 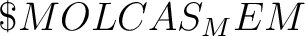 etc. Note that prologue/epilogue scripts should be executable.
For debug purposes, the location of prologue and epilogie files can be set by etc. Note that prologue/epilogue scripts should be executable.
For debug purposes, the location of prologue and epilogie files can be set by
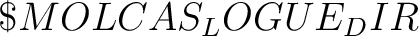 variable. variable.
Example:
prologue:
echo Calculation of $Project input will start at `date`
module.prologue:
echo Running module $MOLCAS_CURRENT_PROGRAM at $WorkDir
Next: 7.3 General input structure. EMIL
Up: 7. The MOLCAS environment
Previous: 7.1 Overview
|





















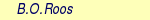

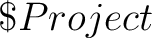 ,
, 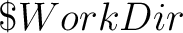 ,
, 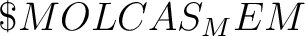 etc. Note that prologue/epilogue scripts should be executable.
For debug purposes, the location of prologue and epilogie files can be set by
etc. Note that prologue/epilogue scripts should be executable.
For debug purposes, the location of prologue and epilogie files can be set by
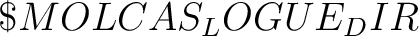 variable.
variable.


 ; export Project
; export Project
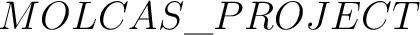 )
)
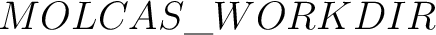 )
)
![[*]](crossref.png)
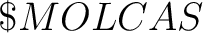 or
or
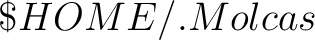 directory. The priority of these settings is: user defined settings
(e.g. in molcas command), user resource file, MOLCAS resource file.
directory. The priority of these settings is: user defined settings
(e.g. in molcas command), user resource file, MOLCAS resource file.
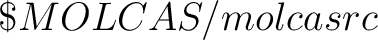 and in
and in
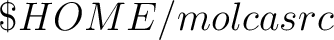 files.
files.